A Development of Cutting Tools in Manufacturing Chronicles
A history of production is deeply intertwined with the evolution of machining tools, which have played a key role in influencing industries and technologies. From the first rock tools used by our ancestors to the advanced machinery of today, the techniques and materials used in cutting have seen significant progress. This journey reflects both technological innovation but also the ever-changing requirements of production methods, efficiency, and precision.
As we explore this development, we must not ignore the emergence of modern machining techniques like laser and waterjet machining methods. These techniques have revolutionized the industrial landscape, offering unmatched precision and flexibility. By harnessing the power of lasers and pressurized water, producers can achieve complex patterns and high-quality results that were previously unthinkable. The narrative of cutting tools is a testament to human ingenuity and the unceasing quest of improving how we mold the materials around us.
Chronological Overview of Cutting Technologies
The evolution of machining technologies can be traced back to prehistoric tools such as carving tools and saws, which formed the basis of production practices. Initial humans utilized simple stone tools to craft materials for tools, weapons, and shelter. As metalworking advanced, so did the machining tools, resulting in the development of bronze and iron blades. These advancements allowed craftsmen to design more complex items with greater precision and efficiency, marking the dawn of manufacturing practices that would evolve over centuries.
With the onset of the Industrial Revolution in the 1700s century, cutting technologies saw a marked transformation. The introduction of steam power led to the introduction of more sophisticated machinery that improved cutting accuracy and production speed. Technologies such as milling machines, lathes, and band saws became essential tools in factories, permitting manufacturers to produce uniform parts on a massive scale. This era set the foundation for modern manufacturing processes, employing cutting as a core method for forming materials.
In the past few decades, the evolution of cutting technologies has sped up with the introduction of computer numerical control, or CNC, and advanced cutting methods such as laser and waterjet cutting service s. These methods have transformed the industry by enabling for exceptionally precise cuts with a variety of materials, from metals to composites. Laser cutting offers rapid precision with minimal material waste, while waterjet cutting utilizes high-pressure water streams to cut detailed designs without thermal distortion. Together, these advancements represent the latest segment in the long history of cutting technologies in production.
Progressions in Laser Cutting Services
Laser cutting techniques has evolved substantially over the last few years, changing the production industry. At first, used for precise cutting in specialized fields, improvements in laser technology have led to their broad use in various sectors. The advancement of powerful CO2 and fiber lasers has facilitated faster cutting speeds, increased accuracy, and the ability to handle a broader range of materials. This transition has allowed manufacturers to meet the growing demands for complex designs and high-quality finishes.
Automation has also played a key role in the evolution of laser cutting services. With the incorporation of computer numerical control (CNC) systems, laser cutting machines now operate with better precision and efficiency. This automation reduces the likelihood of mistakes, simplifies production processes, and allows for intricate geometries to be cut with minimal setup time. As a result, businesses can achieve increased throughput and better utilization of their resources, leading to overall improvements in efficiency and cost efficiency.
Innovative applications in different fields, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device production, have also driven the progression of laser cutting services. Improvements such as 3D laser cutting and the ability to cut mirror-like or thicker materials have enhanced the capabilities of laser cutting technology. These advancements not only enhance the flexibility of laser cutting but also allow manufacturers to pursue new design options, stretching the limits of what can be created in product design and production.
The Emergence of Waterjet Cutting in Production
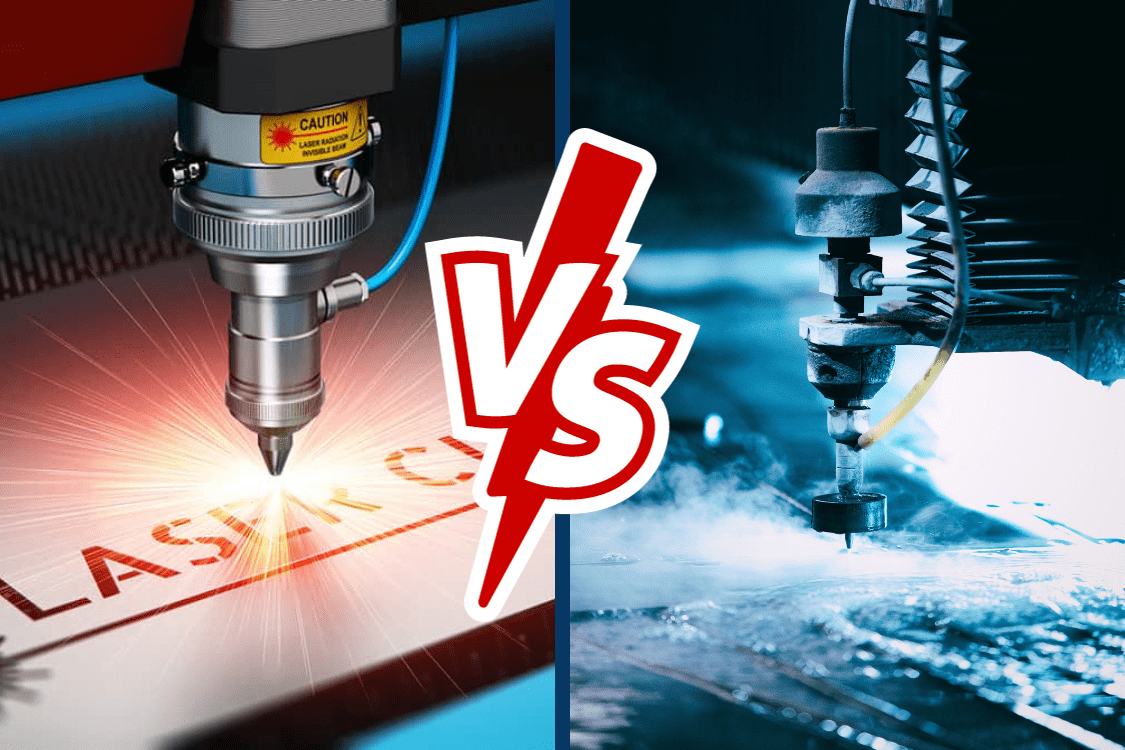
Waterjet cutting has appeared as a revolutionary technology in the industrial industry, offering an advanced alternative to traditional cutting techniques. With its ability to cut through a wide range of materials, including metals, glass, rock, and composites, water-Jet cutting has gained significant traction in industries such as aerospace, auto industry, and structural design. This versatility stems from the cutting process, which utilizes high-pressure water mixed with abrasives to achieve detailed and fine cuts without generating heat, thereby reducing deformation or material degradation.
The expansion of waterjet cutting services has also been fueled by developments in techniques, including upgraded equipment and control systems that allow for increased accuracy and effectiveness. Automation and computer numerical enable manufacturers to create sophisticated designs with minimal loss. Additionally, the sustainable nature of water-Jet cutting, which produces no toxic fumes or dangerous waste, aligns with the industry's rising shift towards sustainability and sustainable practices.
As manufacturers keep to search for ways to enhance productivity and lower costs, waterjet cutting services are becoming a standard in many operations. Its ability to enhance the cutting workflow while maintaining high-quality standards establishes it as a valuable asset in today's industrial landscape. With continuous innovations and growing adoption, waterjet cutting is set to play a pivotal role in the future of manufacturing cutting methods, competing effectively alongside alternative methods such as laser-based cutting.